Radial LayoutDiscover concepts, use cases, and practical customization of the radial layout
The radial layout arranges networks and hierarchies in clear, concentric circles—perfect for highlighting hub-and-spoke structures, central nodes, and relationship distances.
Learn how to visualize your data with radial layouts, explore real-world applications, and unlock advanced diagramming options with yFiles. Try interactive demos, view live coding guides, and see how easy it is to create, style, and adapt hub-centric diagrams for your needs.

What is a radial layout?
The radial layout is a specialized visualization technique that organizes nodes on concentric circles around one or more central focal points. Unlike traditional hierarchical layouts that arrange nodes in horizontal or vertical layers, radial layouts create circular hierarchies where edges primarily point outward from the center, making it ideal for visualizing relationships with clear focal points and distance-based hierarchies.
- Placing important nodes at the center of concentric circles.
- Arranging related nodes on surrounding circular layers.
- Ensuring edges predominantly point outward from the center.
- Creating clear visual representation of topological or conceptual distances.
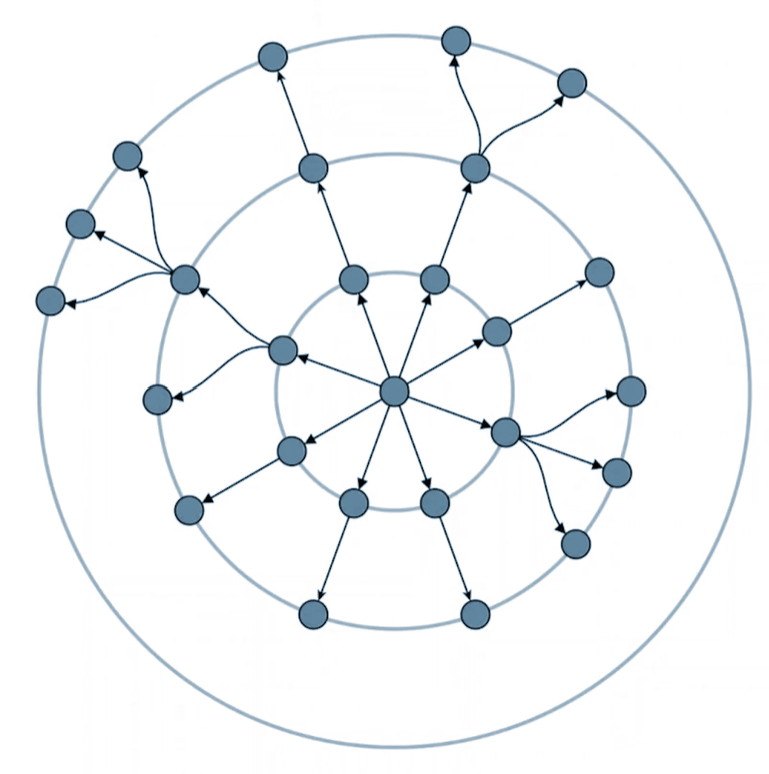
This approach works exceptionally well for tree structures and hierarchical graphs. The algorithm assigns nodes to layers based on distance from center nodes, naturally creating predominantly outward-flowing edges while minimizing tangential connections between nodes on the same layer.
Consider a computer network with a central server. The server sits at the center, directly connected devices form the first ring, devices connected through one hop form the second ring, and so on. This creates clear layers based on actual network distance, with connections flowing primarily from inner to outer rings—exactly how the radial layout algorithm assigns positions based on graph topology.
Create your own radial diagram application
Whether you’re mapping networks with central nodes, visualizing hierarchical data, or exploring hub-and-spoke structures: yFiles’ radial layout arranges your information in clear, concentric circles, accentuating relationships and distances automatically.
The advanced radial layout algorithm places key elements at the center and distributes related nodes to surrounding rings, creating visually engaging diagrams that reveal both structure and connectivity—even for large, complex networks.
Bring your radial diagrams to life with interactive features: reposition central nodes, highlight neighborhoods, customize circular layers, and let users explore connections naturally—on the web, in any framework, and on your platform of choice.
Build your first radial graph application today—for free!
Start now

We´d love to help you. Reach out and we'll get in touch with you.
Your message has been sent.
Use casesReal-world applications of yFiles’ radial layout in technical diagram visualization
From mapping complex gene interaction networks to visualizing social relationships, airport reachability, hierarchical clusters, and organizational charts, the yFiles radial layout creates intuitive diagrams that emphasize central nodes, clarify hierarchical levels, and reveal connection strengths at a glance.
Bioinformatics and computational biology
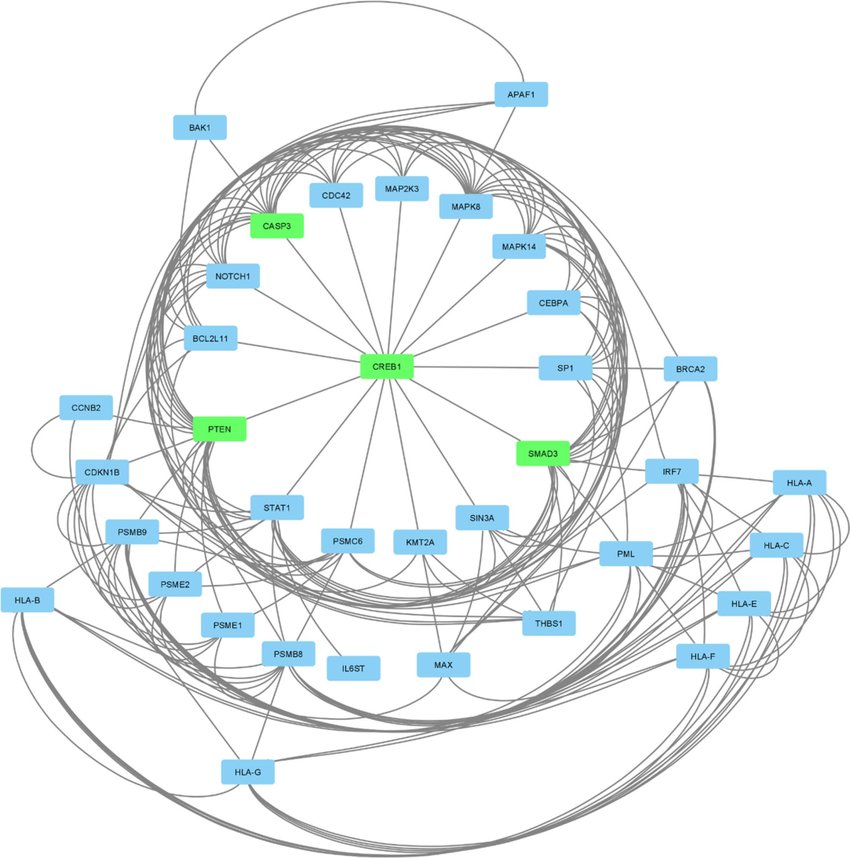
Scientists analyzing links between pancreatic cancer and COVID-19 used Cytoscape with the yFiles radial layout to map complex gene interaction networks. By placing hub genes at the center and radiating related genes outward, the layout created a clear hierarchy that made critical genes stand out instantly.
Color coding highlighted key hubs, enabling rapid recognition of cancer-related pathways and their connections to SARS-CoV-2. This real-world use case shows how yFiles radial layout turns dense biological data into intuitive visual maps, helping researchers prioritize therapeutic targets efficiently.
Social network analysis
Radial layouts excel at visualizing personal networks and relationship mapping:
- Central person placed at the layout center.
- Direct friends on the first concentric circle.
- Friends of friends on subsequent outer circles.
- Distance visualization showing relationship degrees clearly.
The layout provides immediate insight into social connectivity and relationship strength based on topological distance.
Neighborhood circles demo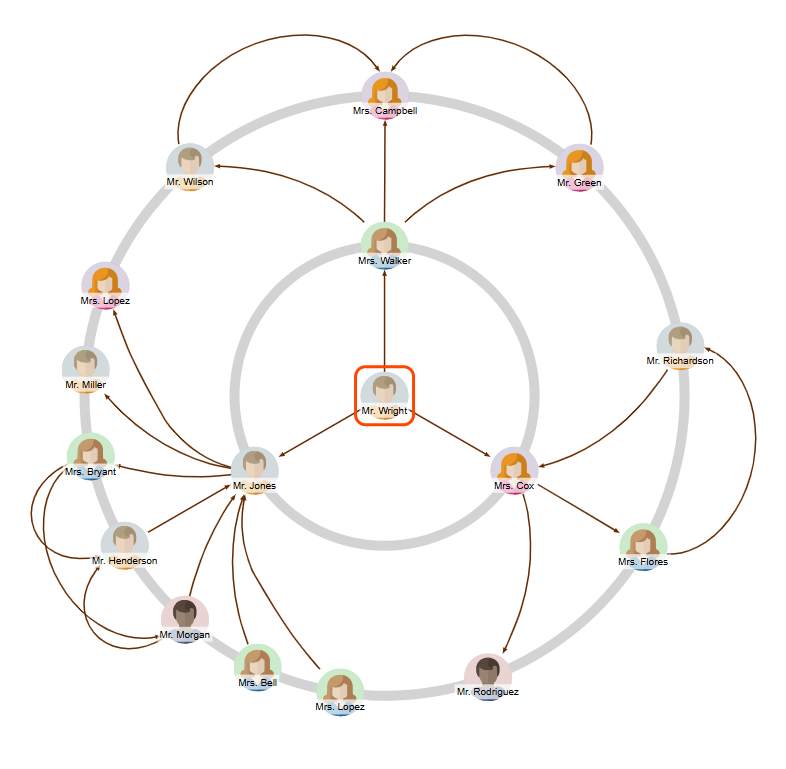
Airport reachability networks
Transportation networks benefit from radial visualization:
- Hub airport (e.g. Frankfurt) positioned centrally.
- Direct destinations on the first circle.
- Connection routes on outer circles based on transfer requirements.
- Transfer visualization clearly showing how many hops are needed to reach destinations.
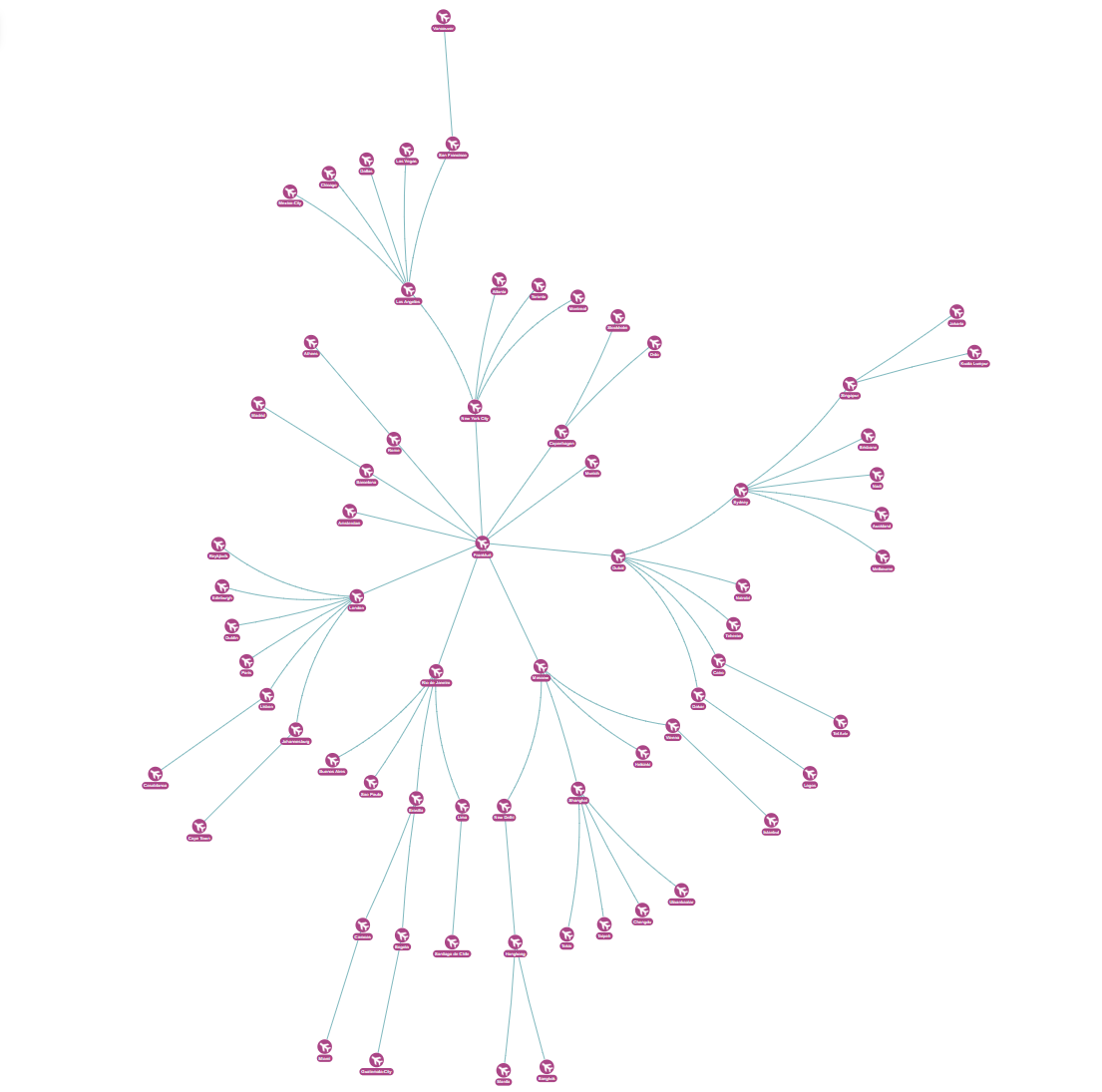
Hierarchical clustering
Scientific and data analysis applications:
- Dendrogram style layouts pushing leaf nodes outward as far as possible.
- Distance-based clustering showing relationships between data points.
- Biological taxonomies like the Tree of Life with interactive exploration.
- Radial labels pointing toward center for compact, readable displays.
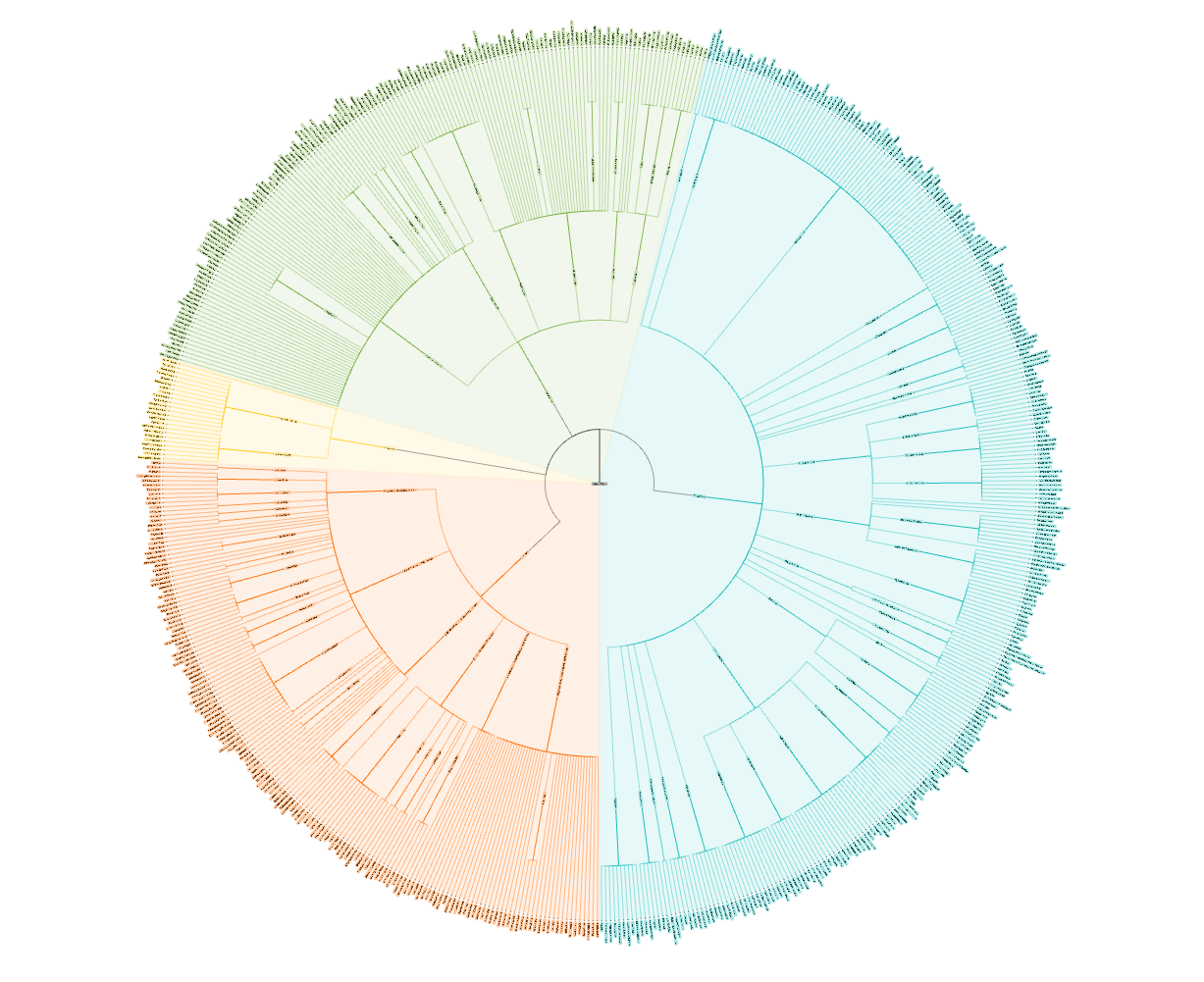
Organization charts and reporting structures
Corporate hierarchy visualization:
- Leadership positioned centrally.
- Management layers on successive circles.
- Reporting relationships clearly defined through radial structure.
- Department groupings organized by sectors within circles.

When to choose the radial layout
Radial layouts are ideal whenever you need to highlight central nodes and their connections across a network. Unlike other layouts, they emphasize hub-and-spoke relationships, making complex networks easier to interpret at a glance.
The table below compares radial layout applications across industries and data types, showing when it’s the best choice versus alternative layouts:
| Use case | Why radial layout? | Alternative layout | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social networks | Shows relationships clearly | Organic layout | Personal networks, influence mapping |
| Bioinformatics | Highlights hub genes and pathways | Hierarchical layout | Protein interactions, gene networks |
| Transportation | Hub-and-spoke visualization | Hierarchical layout | Airport networks, route planning |
| Organizations | Clear hierarchy with central leadership | Tree layout | Company structures, reporting lines |
| Knowledge maps | Core topics with related concepts | Tree layout | Research areas, topic clustering |
Core principles of the radial layoutTake control of structure and clarity
The radial layout organizes complex networks into a clear, hub-and-spoke structure by following a few fundamental principles. It begins with center selection, identifying one or more central nodes that serve as the network’s focal points.
Next, layer assignment arranges connected nodes in concentric circles or rings around the center, while angular positioning distributes nodes evenly along each ring.
Finally, edge routing connects the nodes using paths that maintain clarity and highlight relationships, creating an intuitive visualization of hierarchical or interconnected data.
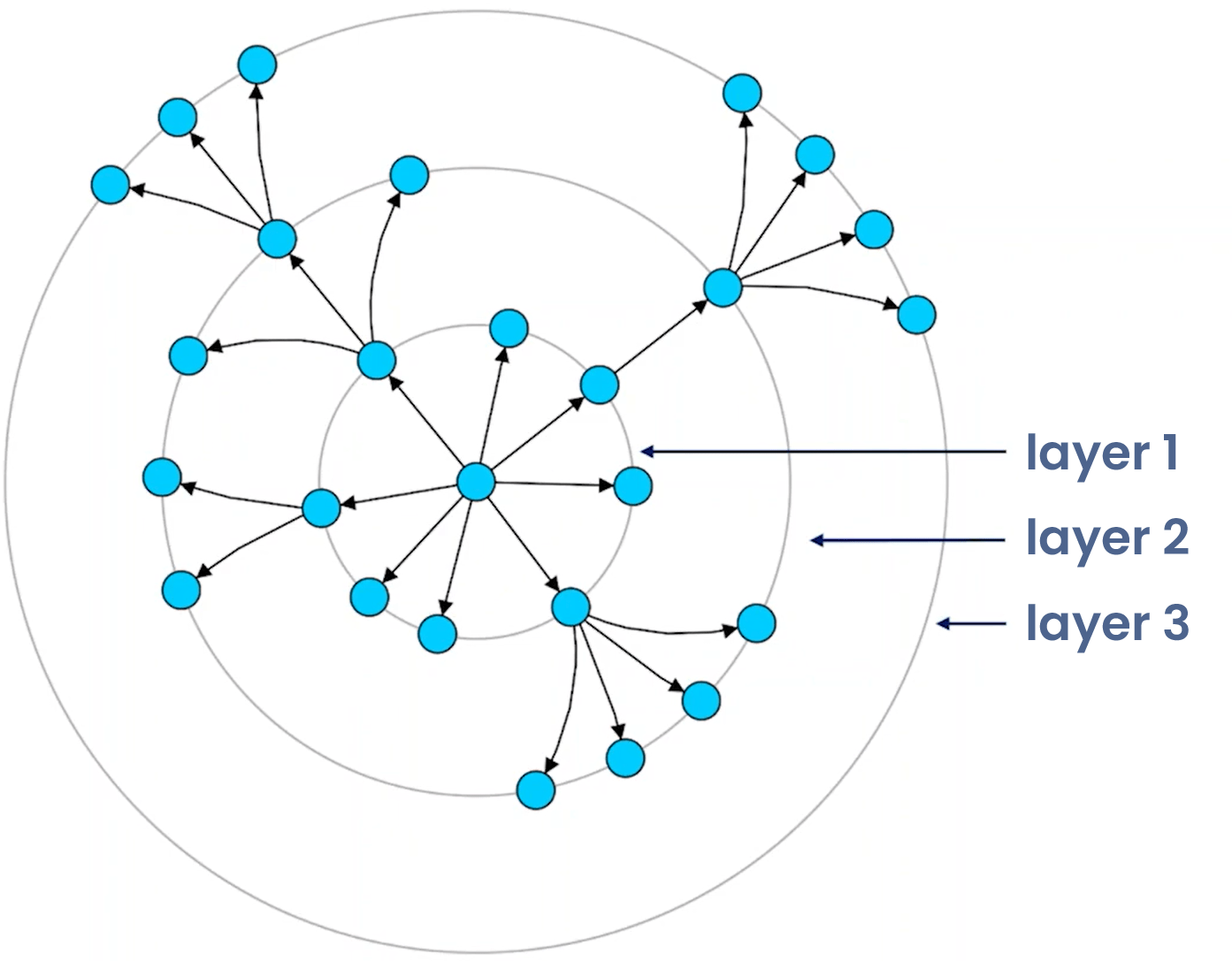
The process generally involves these stages:
- Center selection: Choosing the central node(s).
- Layer assignment: Organizing nodes in concentric circles/rings.
- Angular positioning: Distributing nodes around each ring.
- Edge routing: Connecting nodes with appropriate paths.
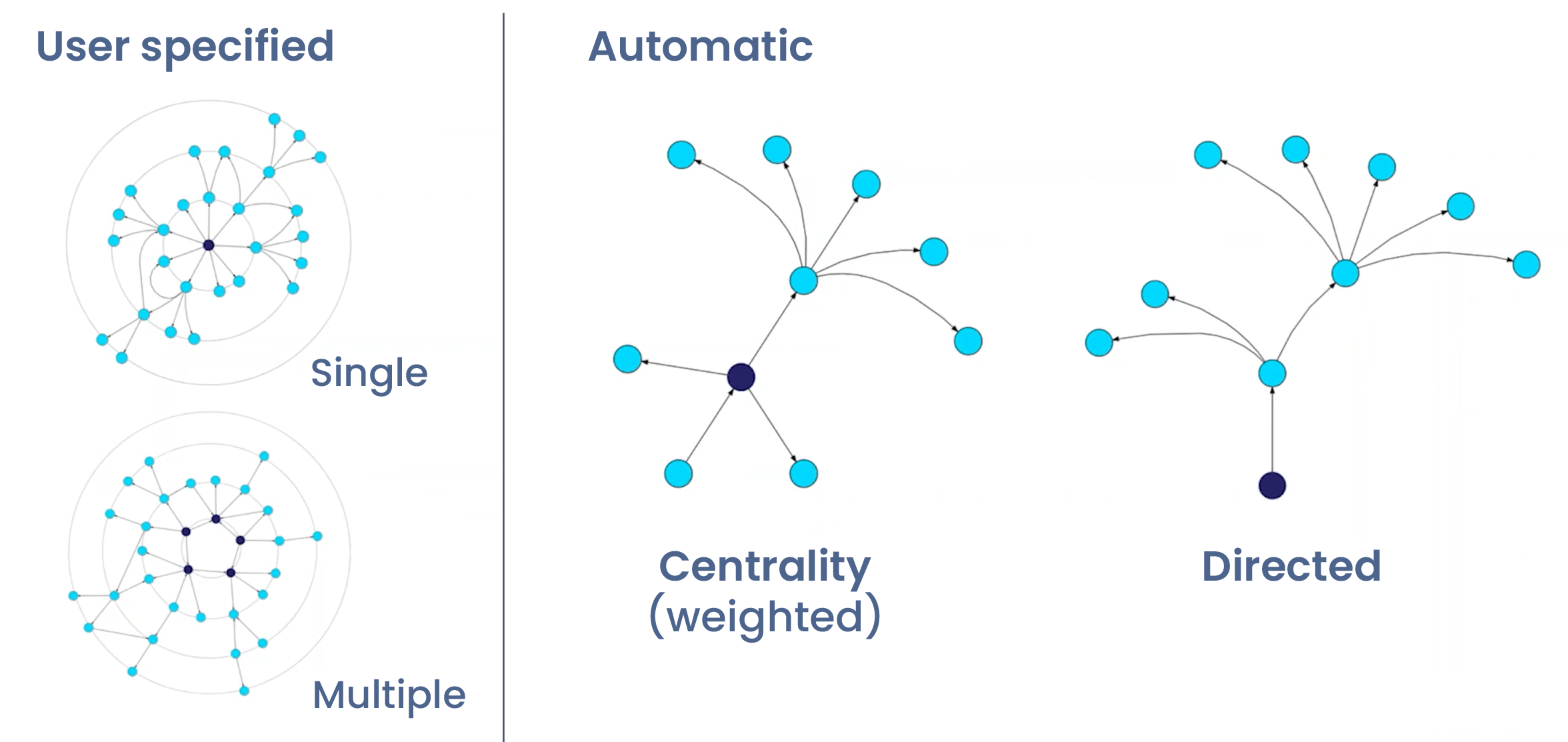
Center selection
The layout algorithm first creates a virtual tree from the input graph:
- Center node selection using various strategies (centrality, directedness, custom). It's possible to have more than one center node.
- Tree derivation ensuring all edges point outward when possible.
Layer assignment
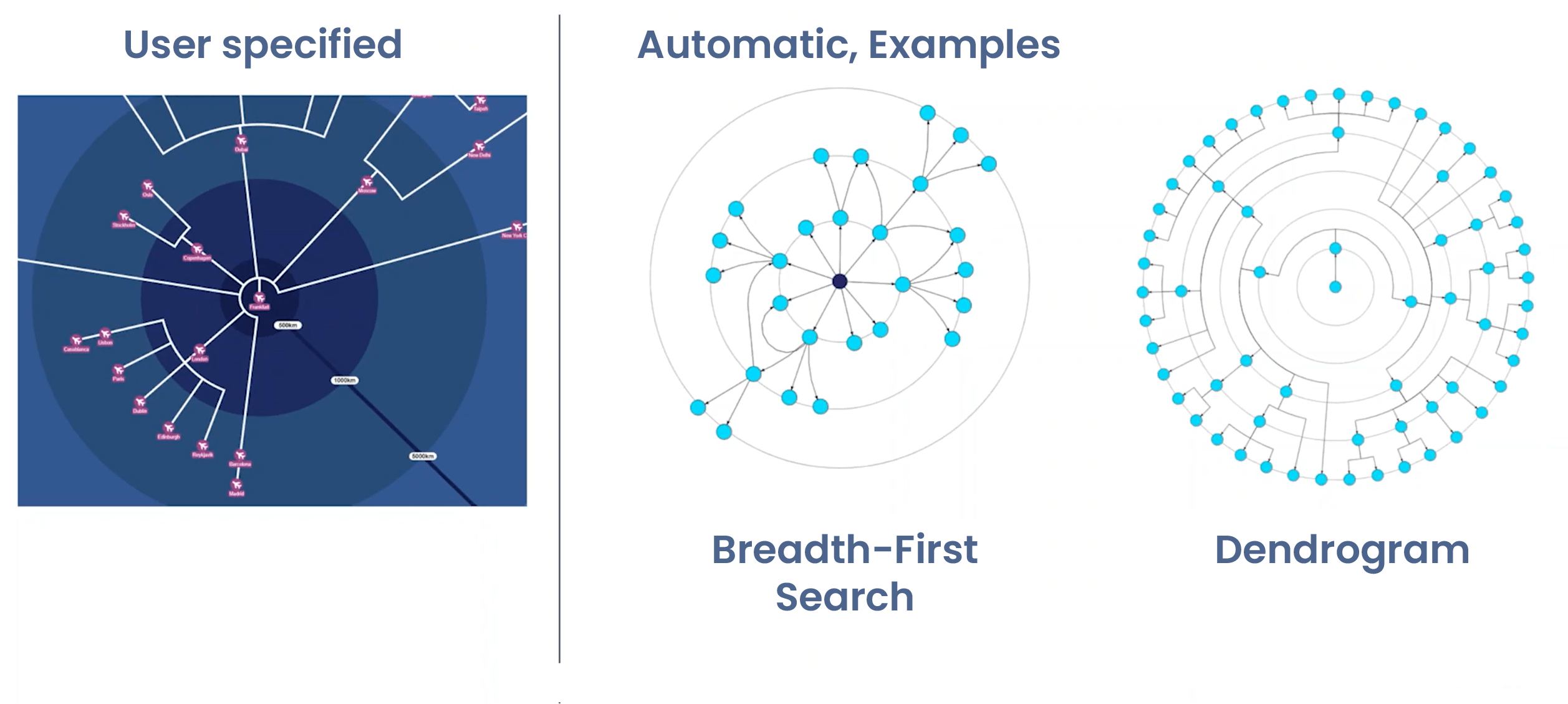
Nodes are organized into concentric circles using several automatic strategies:
- Breadth-First Search (BFS): Starting from center, assign nodes to layers based on graph distance (central node -> to neighbours -> to the neighbours of these neighbours ...).
- Dendrogram style: Push nodes as far outward as possible, maximizing radial spread.
- Centrality-based: Use graph centrality measures to determine optimal center nodes.
Angular positioning
- Distribute nodes evenly along each concentric circle.
- Optionally adjust angles to reduce overlaps or emphasize certain connections.
- Angular positioning complements layer assignment to create a balanced radial structure.

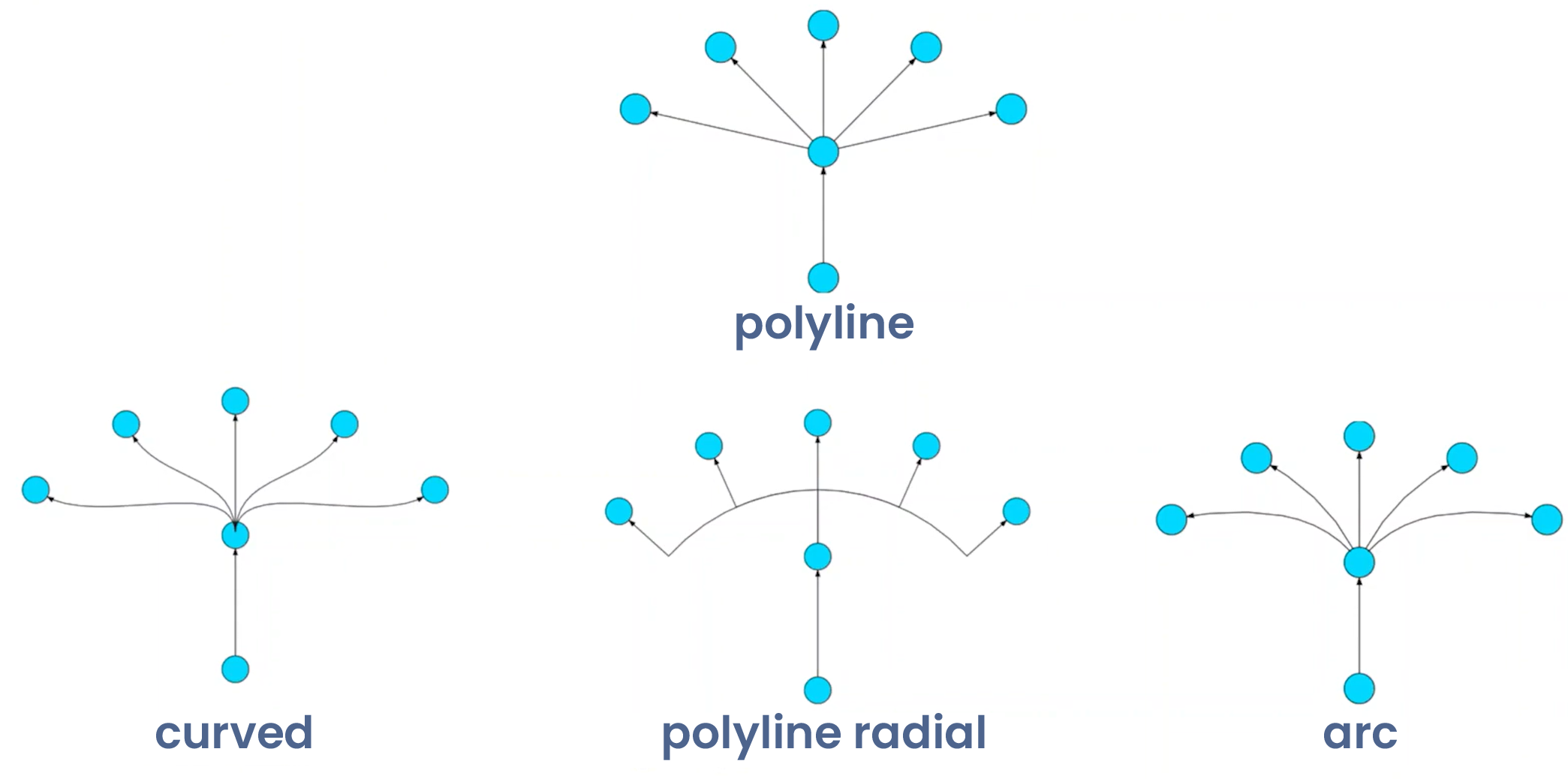
Edge routing
For radial/hub-spoke layouts, use curved edges (Bezier, arc, or cardinal splines) that follow the natural radial flow from hub to nodes, maintaining the circular structure's visual coherence.
In dense networks, apply edge bundling to group similar trajectories and reduce clutter while preserving hub-to-node relationships. Alternatively, use radial-polylines with waypoints that respect the circular geometry.
The key principles are ensuring all edge routing reinforces the radial structure with the hub as the central organizing element, minimizing edge crossings in the radial context, and maximizing both readability and the layout's inherent ability to highlight centralized network topologies.
User-defined customization strategies
The radial layout in yFiles supports user-defined strategies that give developers fine-grained control over how nodes are arranged. For instance, nodes can be assigned to specific layers according to custom rules, ensuring the layout reflects meaningful hierarchies or classifications.
Additionally, the layout allows manual specification of the central node, giving precise control over the focal point of the network and ensuring that the most important elements are emphasized.
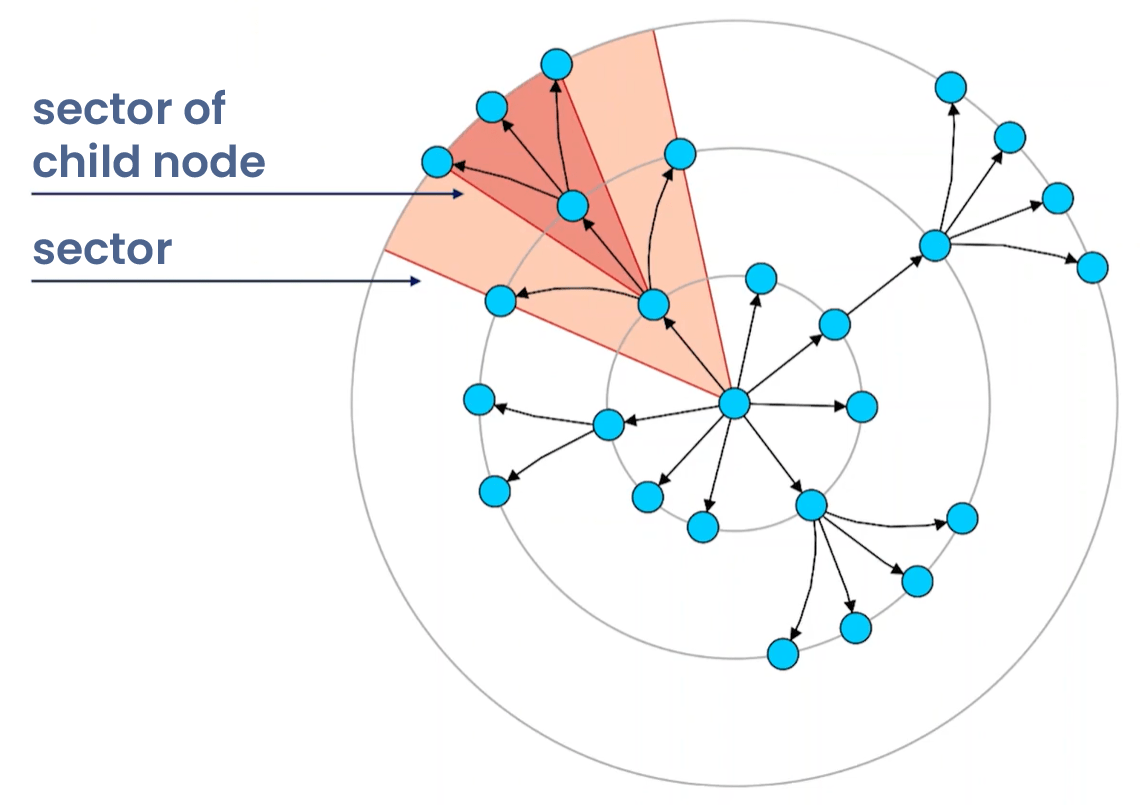
Sector management
The layout uses sectors to organize and separate different branches:
- Sector definition: Angular regions defined by leftmost and rightmost nodes in subtrees.
- Containment rule: Child sectors must be contained within parent sectors.
- Non-overlapping constraint: Independent subtrees receive separate, non-overlapping sectors.
Rule 1
Sector of a child node is part of the sector of its parents.
Rule 2
Sectors of independent sub-trees do not overlap.
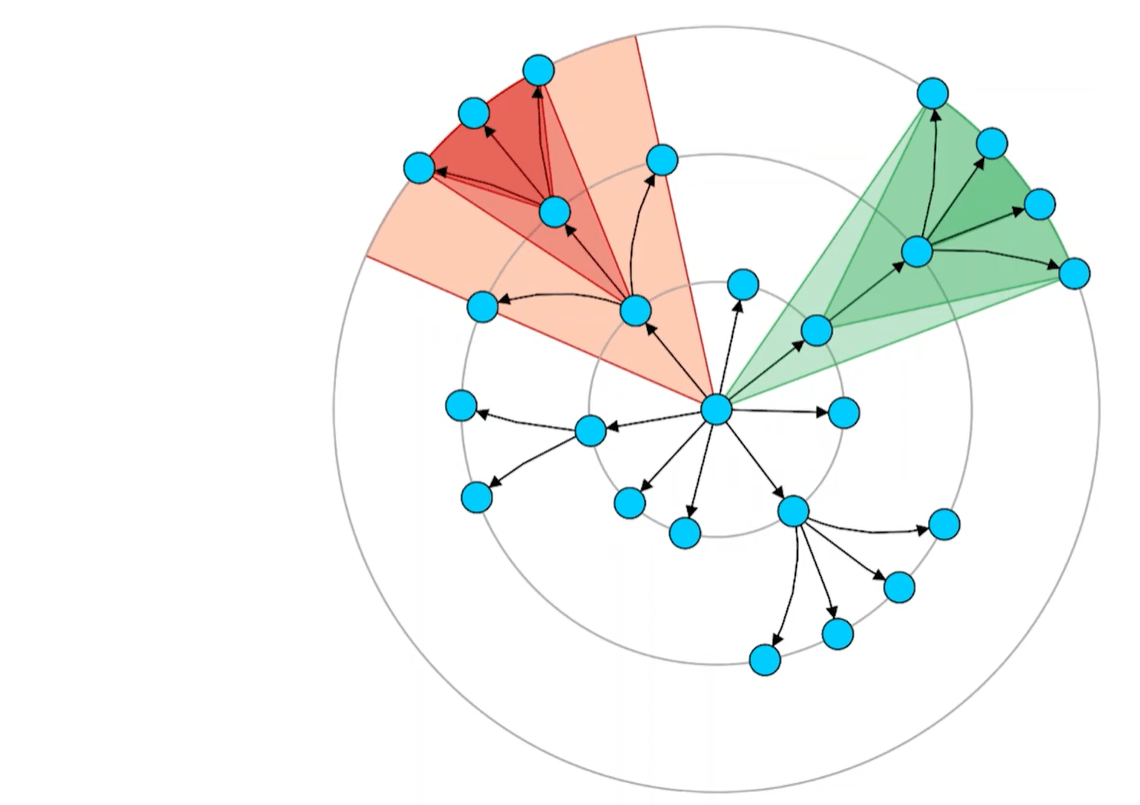
This sector system ensures clean separation of different hierarchical branches while maintaining the radial structure.
Label management
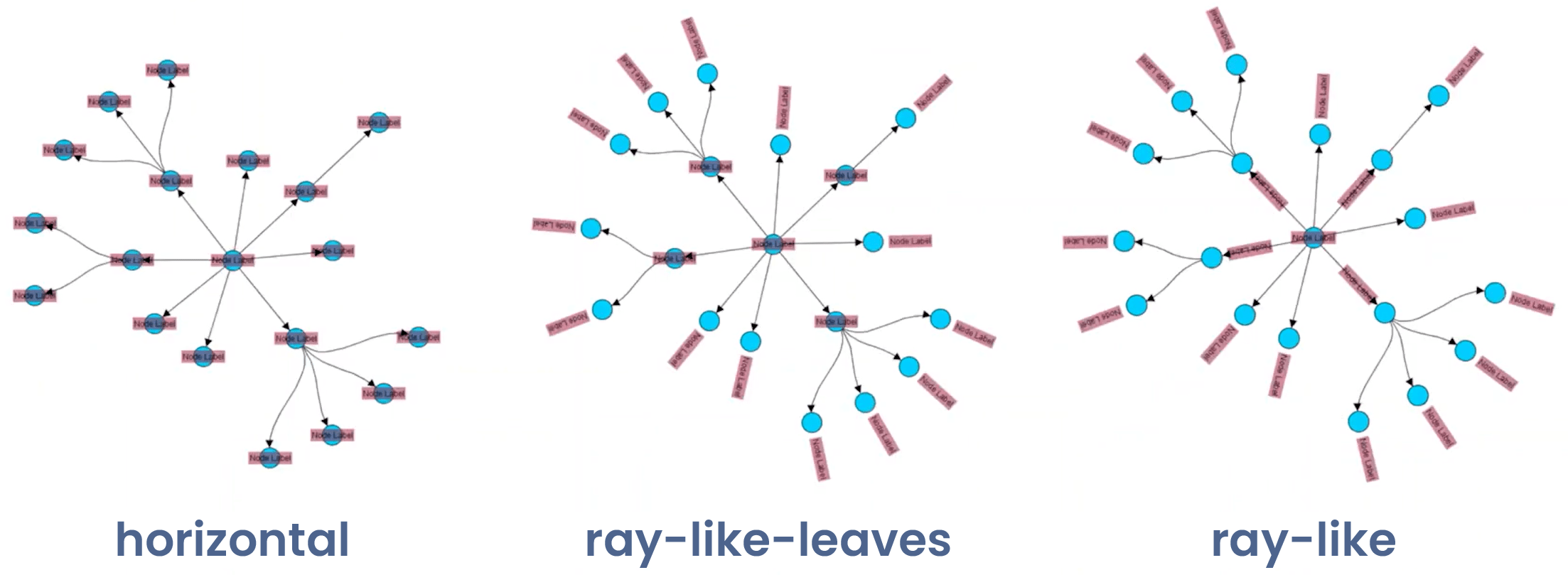
Specialized automatic node labeling for radial layouts keeps networks clear and readable. Node labels can be horizontal for standard orientation, radial pointing toward or away from the center, or ray-like aligned with edges toward the hub.
The layout also offers generic edge labeling, automatically placing edge labels on suitable positions to maintain a clean, organized visualization.
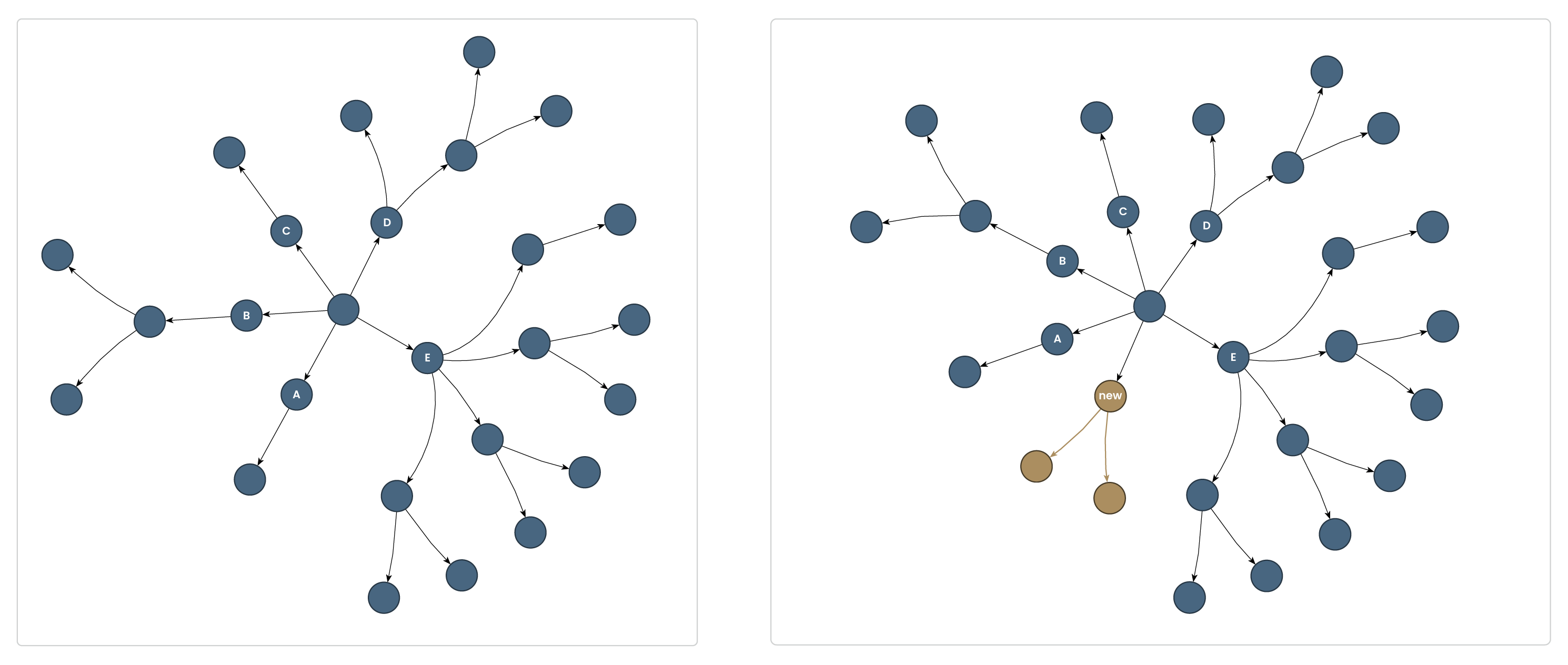
Custom node order
yFiles’ radial layout supports customizing the order of child nodes—both for initial layouts and dynamic changes—using the childOrder property. This lets you precisely define the cyclic arrangement of children in tree-like graphs, helping preserve important visual patterns, group related nodes, or maintain a consistent user experience as data evolves as/like in incremental layouts.
Concepts recap
| Concept | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Center selection | Choose central node(s) as layout anchor points |
| Layer assignment | Organize nodes in concentric rings by distance/importance |
| Angular positioning | Distribute nodes around each ring to minimize crossings |
| Edge routing | Control connection paths (straight, curved, bundled) |
| Specialized labeling | Handle labels within layout to avoid overlaps |
| Custom node order | Define or preserve the cyclic order of child nodes |
Watch the full webinar episode
Watch the full episode below to gain a comprehensive understanding of radial layouts in yFiles. Dr. Benjamin Niedermann walks you through the core concepts and provides practical demonstrations.
Explore more resources:
Watch the full episode below to gain a comprehensive understanding of radial layouts in yFiles. Dr. Benjamin Niedermann walks you through the core concepts and provides practical demonstrations.

Explore more resources:
Interactive radial layout demos
Discover a selection of interactive demos showcasing different radial layout features in yFiles. Explore how various layout options help visualize complex structured data clearly and intuitively.
Step-by-step guideHow to create a radial layout with yFiles
Creating a radial graph layout with yFiles takes just a few steps:
1. Create the network from business data
2. Make information visible
3. Improve arrangement
4. Apply different layout options
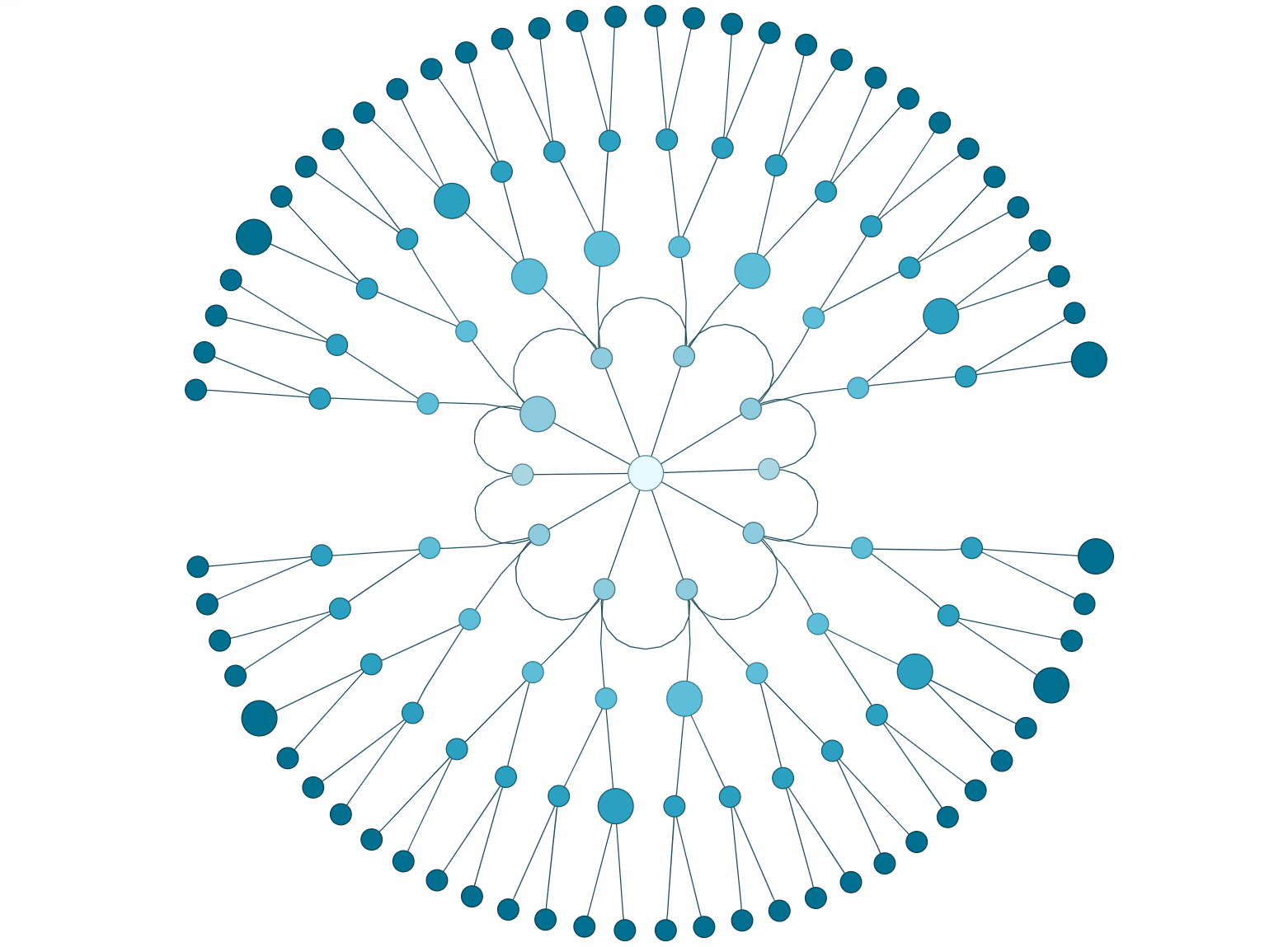
Interactive radial layout playground
The Playground lets you experiment with yFiles' radial layout interactively. Create, edit, and style graphs, adjust layout parameters, and see results instantly—all in one online IDE. Discover how easy it is to prototype and design graph-based applications with yFiles.
graph.nodeDefaults.size = [70, 70];
graph.nodeDefaults.style = new ShapeNodeStyle({
shape: ShapeNodeShape.ELLIPSE,
cssClass: "node",
});
graph.nodeDefaults.labels.style = new LabelStyle({
shape: LabelShape.PILL,
backgroundFill: "white",
backgroundStroke: "1px solid #6A8293",
font: "15px poppins",
textFill: "#6A8293",
});
graph.edgeDefaults.labels.style = new LabelStyle({
shape: LabelShape.PILL,
backgroundFill: "#6A8293",
backgroundStroke: "1px solid white",
font: "15px poppins",
textFill: "white",
});
graphComponent.fitGraphBounds()Why use yFiles' radial layout?Unique capabilities for radial layouts you won’t find in other SDKs.
While many software development kits (SDKs) can generate radial layouts, only yFiles provides these game-changing advantages, like edge bundling, and custom node order:
The yFiles radial layout can handle a lot of data by creating a compact, concentric-circle visualization. It's also highly customizable, giving you precise control over a graph's structure and appearance.
All of this runs efficiently on yFiles’ robust engine, capable of handling thousands of nodes with smooth, real-time layout updates and animations.

Frequently Asked Questions
Recap
Radial layout

Radial layout is a graph visualization technique that arranges nodes in concentric circles around one or more central hubs, emphasizing hierarchical structure, relationship distance, and network centrality. This approach is especially effective in scenarios like bioinformatics, social networks, organizational charts, and transportation systems, where highlighting hub nodes and their connections is crucial for intuitive analysis.
The yFiles SDK offers a sophisticated radial layout algorithm with extensive customization features. Developers can define central nodes, layer assignments, sector management, and edge routing strategies, making it easy to tailor the visualization for hub-and-spoke, dendrogram, or clustered data structures. As explored in about radial layout and core principles, yFiles supports interactive features, dynamic updates, and advanced labeling—all designed to help users highlight relationships, clarify distances, and navigate large and complex networks efficiently. See the Key Benefits section for more reasons to choose yFiles’ radial layout.
For practical integration insights and inspiration, visit dedicated sections on use cases and step-by-step guide or try out interactive examples like the Neighborhood Circles Demo and Radial Airports Demo.







