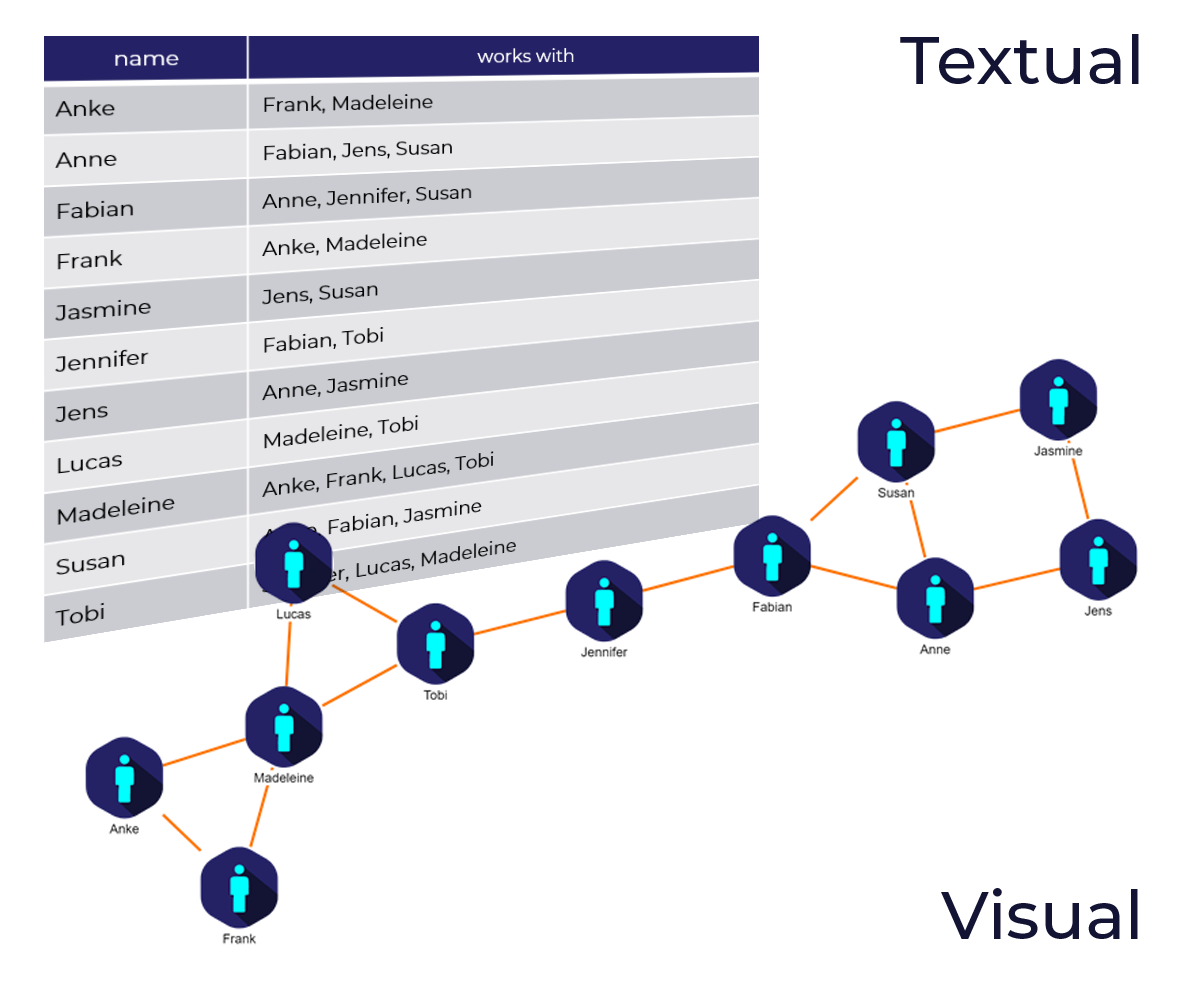
Visualizing Graph DatabasesLearn to visualize a graph database and how users benefit from a graphical representation
A graph database uses a collection of nodes and edges with associated properties to store data. In contrast to table-based, or relational databases, graph databases can handle huge amounts of connected data more efficiently because only locally connected parts of the database need to be considered when running queries on the database. This approach makes them particularly useful in big data analysis. Commonly used graph databases are Neo4j, Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB, OrientDB etc.
Their data storage approach that focuses on relationships can be used to create a graphical representation in the form of a diagram.
A visualization enables users to visually explore the stored data, identify significant structures, and get a better understanding of relationships. Besides the visual exploration, it is also possible to interactively edit the stored data by modifying the diagram without any in-depth knowledge of the underlying storage technology or query language (e.g., Cypher, GraphQL, Gremlin or SPARQL). For example, new nodes and relationships can be created using mouse gestures. Therefore, visualizing a graph database is a powerful solution when handling or analyzing vast amounts of data.
Powerful Graph Visualizations with yFiles
yFiles gives you the tools to create clear and scalable graph visualizations for graph databases. With advanced automatic layouts, you can focus on analyzing and optimizing your graph data instead of arranging nodes manually.
Leverage interactive features, animations, and flexible styling to build dynamic graph applications. yFiles seamlessly integrates with web technologies, making it easy to bring data to life in any application.
Start visualizing your database graphs with yFiles today!
Prototype your own graph application

We´d love to help you. Reach out and we'll get in touch with you.
Your message has been sent.
Challenges of graph database visualizations
Although the nature of the connected graph data is predestined for visualization, it is still a challenging task because of the sheer amount of data that it usually contains.
The first step in presenting the data is to query it from the database. After that, the query result must be arranged meaningfully to create a human-readable representation of the raw data. Additionally, a styling that differentiates the different types of entities and relations and presents the properties associated with the items helps to interpret the data at a glance. Furthermore, the performance should allow for an interactive exploration of the data.
Visualizing a graph database
Most graph databases provide a basic visualization of the stored data through their particular client application. These graphical representations usually allow the user to see parts of the stored entities and relations alongside associated properties. Some data explorers also provide means to edit the stored data in their graphical user interface.
However, the built-in explorers are often limited in the amount of data they can display at once, or they provide only a relatively simple representation and interaction. Sometimes it is required to tailor the visualization, user interaction, and automatic layout of the data for a specific use case, which is not possible with the built-in solutions, or the graph database does not come with any graphical representation at all.
Utilizing a sophisticated visualization solution
A comprehensive visualization solution provides a means to create a client that enables users to gain more insight into the stored data. It can be tailored to specific requirements related to element visualization, element arrangement, or interactions.
yFiles is a commercial programming library explicitly designed for diagram visualization and is a perfect fit for the challenges of graph database visualization. The sophisticated layout algorithms of yFiles can easily transform the data into a readable, pleasing, and informative network. The different layout styles, for example, organic, hierarchic, circular, radial, orthogonal, or tree, enable the user to intuitively identify structural characteristics of the data, such as hierarchy, connected components, or rings.
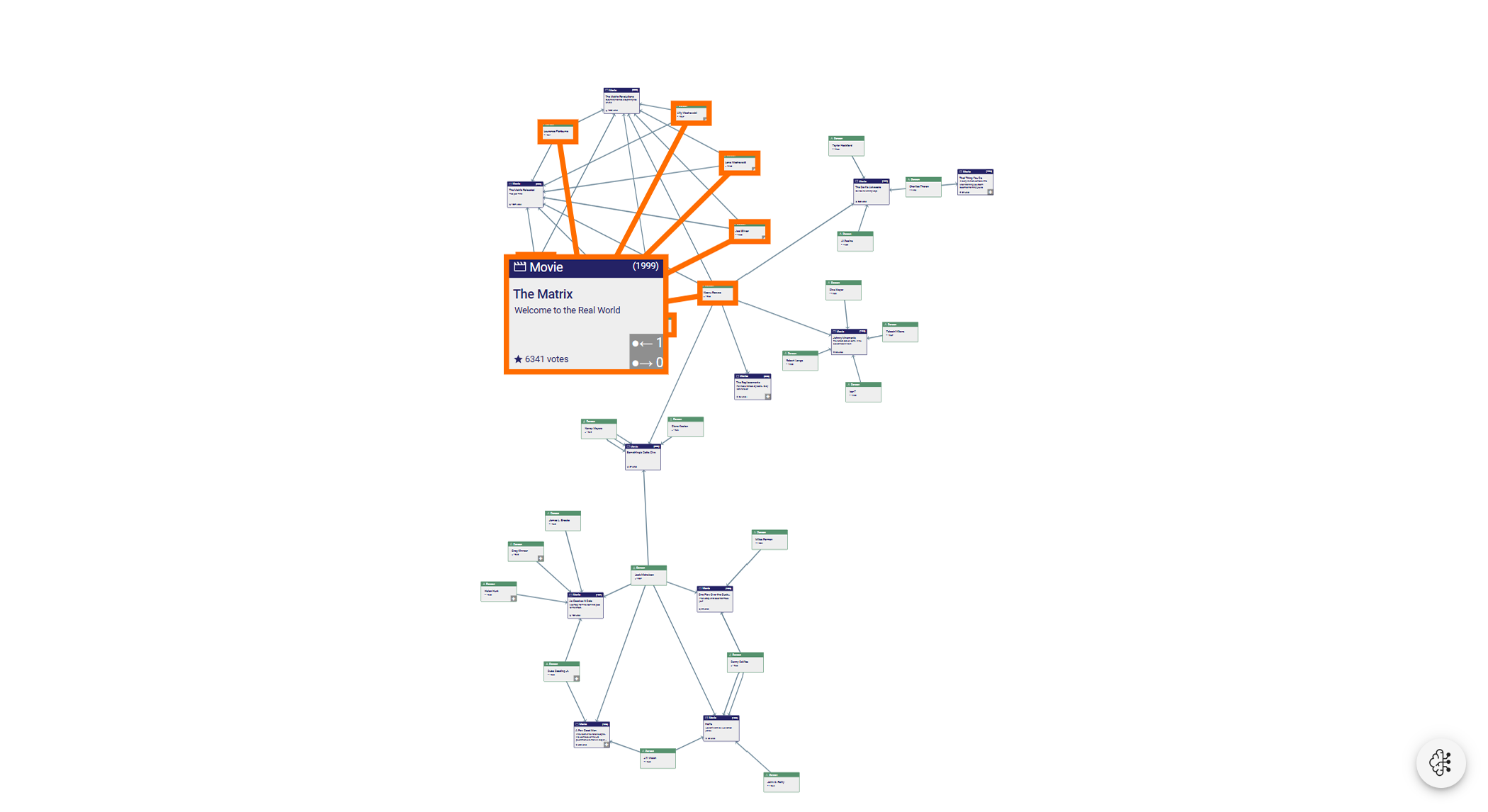
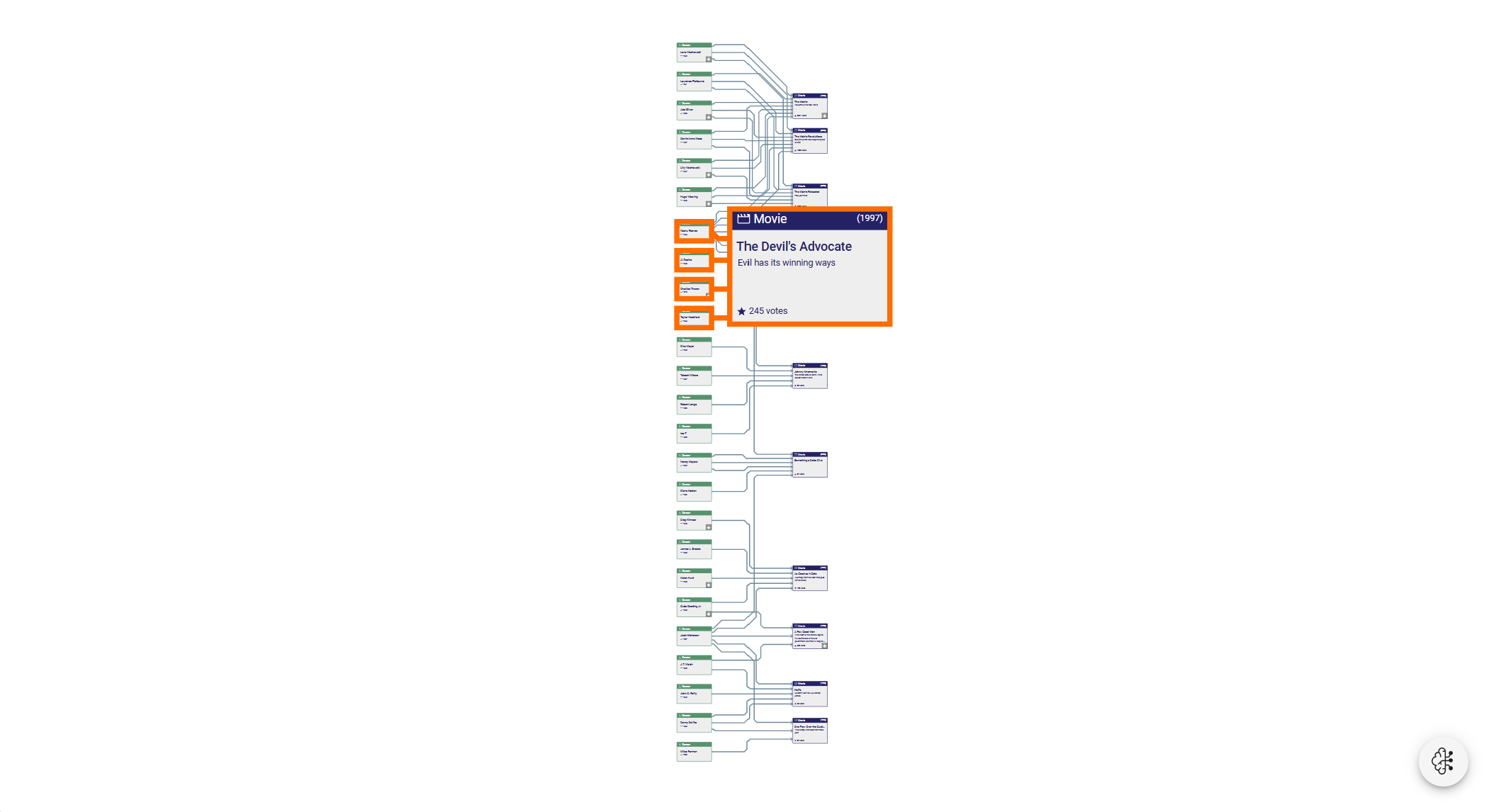
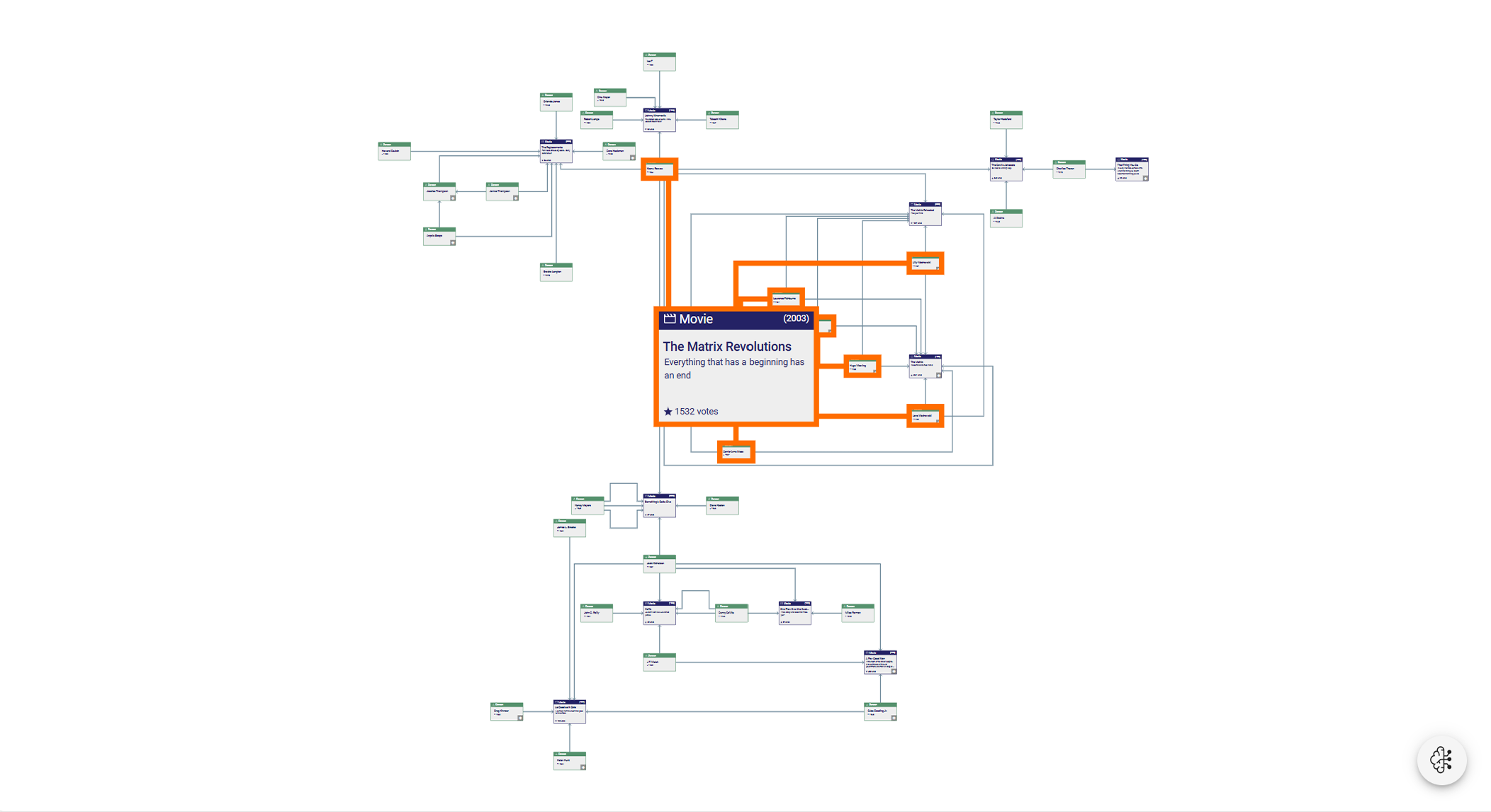
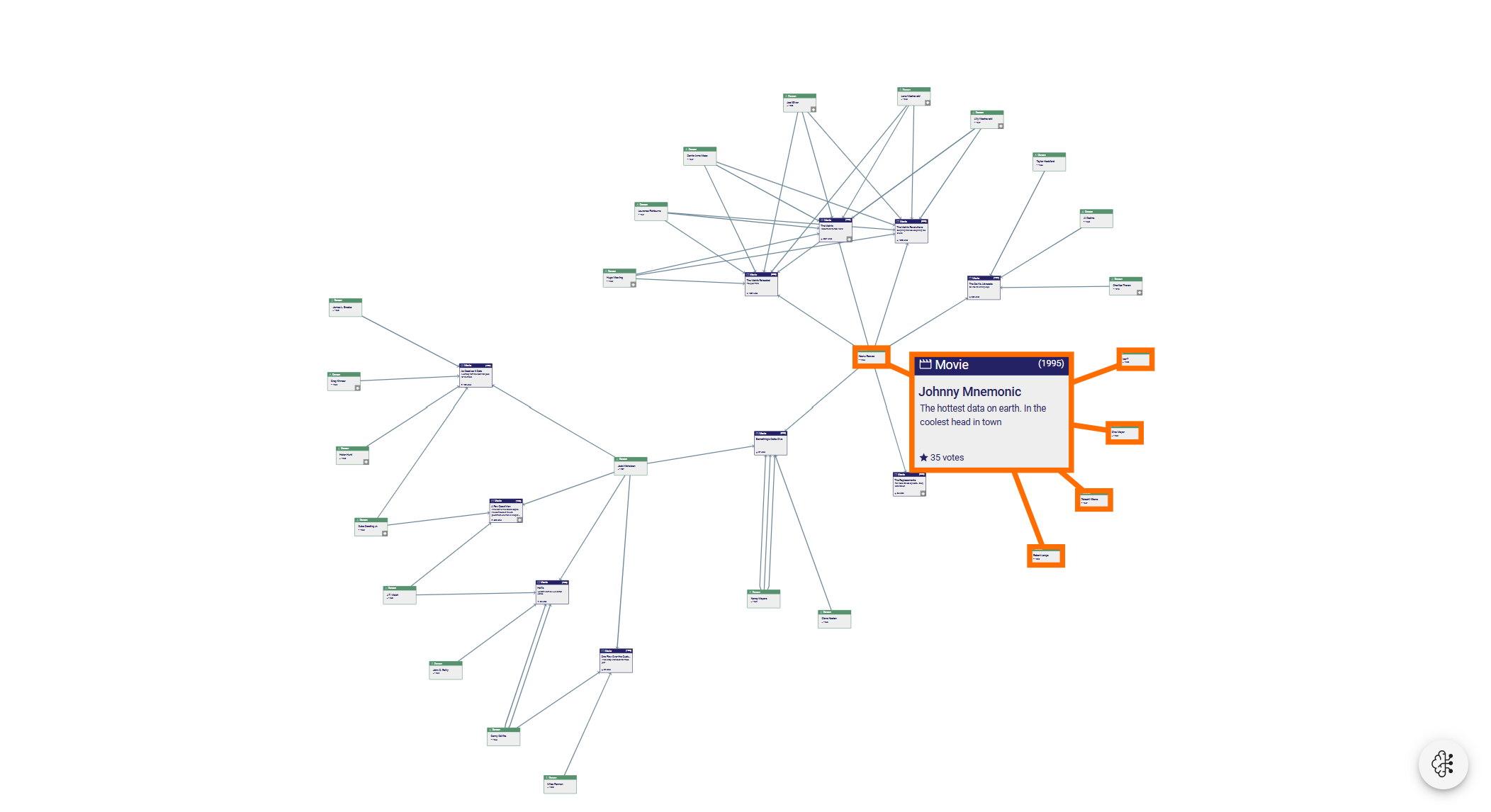
Visual representations of different database types
Furthermore, yFiles for HTML comes with a multiplicity of graph analysis algorithms (e.g., centrality, clustering, path algorithms, etc.) that can be applied to the data model to add more value to the data.
In a neatly arranged diagram, users can easily navigate and edit the relationships and data objects with the powerful interaction handling that yFiles provides out of the box. The library is also fully customizable and extensible to support scenarios where interactive drill-down exploration is needed to focus the user’s attention on local parts of a huge diagram.
The relationships and data objects can be rendered with the node and edge styles that come with yFiles, which already offer a wide range of properties to tailor the style for a particular use case or branding. If this is not sufficient, it is always possible to create an entirely custom visualization that perfectly fits the given data.
Which data sources can be used?
Graph databases come with different query languages (e.g., GraphQL, Cypher, Gremlin, SPARQL, SQL, etc.) that all yield data in a slightly different format. A generic data interface can be connected to arbitrary data sources such that the different query results can be transformed into a graph model.
This generic approach allows yFiles to augment any graph database, for example Neo4j, Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB, OrientDB.
About yFiles: The graph visualization SDK
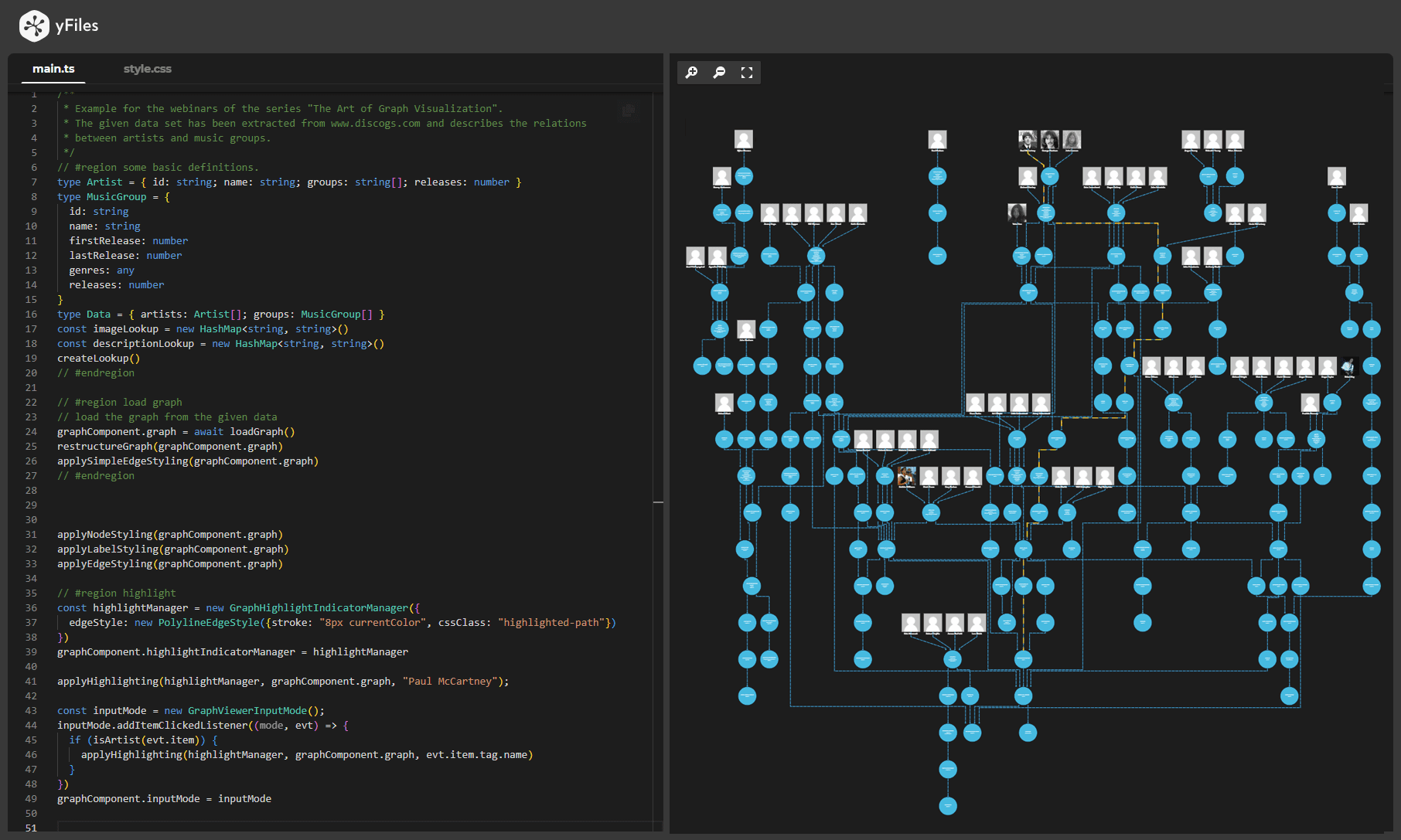
yFiles is your go-to SDK for crafting advanced graph visualizations, whether you're working with Web, Java, or .NET technologies. Its unmatched flexibility and scalability enable you to convert complex data into clear, actionable visuals, fitting for both enterprise and startup needs.
With yFiles, you're equipped for the future—supporting any data source while maintaining strong data security. Getting started is seamless, thanks to over 300 source-code demos, thorough documentation, and direct access to core developer support. These resources are available even during your free trial.
Backed by 25 years of graph drawing expertise, yFiles is trusted by top companies worldwide for their most critical visualization tasks.
Discover yFiles11 reasons why graph database developers trust yFiles!

yFiles Newsletter
Stay informed about yFiles, network visualization, and graph technology updates.
Join our newsletterWebinar: How to visualize database content with yFiles
This webinar demonstrates how to visualize a Neo4j database with yFiles for HTML in a simple web application built with JavaScript:
More information is also available in this blog post.
Examples and source code
With yFiles, database visualization can be realized on all supported platforms. yFiles for HTML comes with a Neo4j Sample Application and a GraphQL Sample Application that show how to load data from a Neo4j database and a GraphQL service, respectively.
The source code of these sample applications is part of the yFiles for HTML package and available on the yWorks GitHub repository:











